 सोमवार - शनिवार: सुबह 9.00 बजे - शाम 6.00 बजे
सोमवार - शनिवार: सुबह 9.00 बजे - शाम 6.00 बजे सोमवार - शनिवार: सुबह 9.00 बजे - शाम 6.00 बजे
सोमवार - शनिवार: सुबह 9.00 बजे - शाम 6.00 बजेBS EN 1377-9 DENSITY SAND
उत्पाद विवरण:
- रंग
- वज़न किलोग्राम (kg)
- रेत का प्रकार
- रेत की सुंदरता
- फ़ीचर , ,
- अधिक देखने के लिए क्लिक करें
मूल्य और मात्रा
- आईएनआर
- 3
उत्पाद की विशेषताएं
- किलोग्राम (kg)
व्यापार सूचना
- प्रति दिन
- दिन
- Yes
- 25 Kg Bag
- , , , , , , , ,
उत्पाद वर्णन
BS 1377 is a comprehensive set of British Standards that outlines various methods of test for soils for civil engineering purposes. When discussing "density" within the context of BS 1377, it refers to the unit weight of the soil, which is a fundamental property used in geotechnical engineering for design and earthwork assessment.
Density and its Description in BS 1377
In general, BS 1377 covers different aspects of soil density, including:
Definitions of Density:
- Bulk Density (\rho_{b} or \gamma_{b}): This is the total mass (or weight) of a soil per unit volume, including the solid particles, water, and air voids. It is influenced by the moisture content and the degree of compaction. It is typically expressed in Mg/m$3$ (megagrams per cubic meter) or kg/m$3$ (kilograms per cubic meter) for mass density, or kN/m$3$ (kilonewtons per cubic meter) for unit weight.
- Dry Density (\rho_{d} or \gamma_{d}): This is the mass (or weight) of the solid particles of a soil per unit total volume of the soil. It excludes the mass of water. Dry density is a crucial parameter for assessing the degree of compaction achieved in earthworks.
- Particle Density (\rho_{s} or G_{s}): Previously known as "specific gravity" of soil solids, this refers to the density of the actual solid particles themselves, excluding any voids. Its the ratio of the mass of soil solids to the mass of an equal volume of water. Its typically determined using a density bottle or pycnometer.
Methods for Determining Density:
BS 1377 specifies various methods for determining these densities, both in the laboratory and in situ:
- Compaction Tests (e.g., BS 1377-4:1990, now consolidated in BS 1377-2:2022): These tests determine the relationship between the moisture content and the dry density of a soil when a specific compactive effort is applied. The aim is to find the optimum moisture content (OMC) at which the maximum dry density (MDD) can be achieved. Common methods include:
- 2.5 kg rammer method (Standard Proctor Test): Uses a 2.5 kg rammer falling from a height to compact soil in a mold.
- 4.5 kg rammer method (Modified Proctor Test): Uses a heavier 4.5 kg rammer and greater drop height, providing a higher compactive effort.
- Vibrating hammer method: Primarily for granular soils, using a vibrating hammer to achieve compaction.
- Maximum and Minimum Densities of Granular Soils (BS 1377-4:1990): These tests determine the loosest and densest states a granular soil can achieve in a laboratory setting. These values are used to calculate the relative density (density index).
- Particle Density (Specific Gravity) Determination (BS 1377-2): Methods involving density bottles or pycnometers to find the density of the solid particles.
b) In-Situ Tests (BS 1377-9:1990):
These methods determine the density of soil as it exists in the ground.
- Sand Replacement Method (small and large pouring cylinders): This is a very common method. A hole is excavated in the ground, and the excavated soil is weighed. The volume of the hole is then determined by filling it with a standard sand of known bulk density.
- Core Cutter Method: Used for cohesive soils, where a cylindrical cutter is driven into the ground to obtain a sample of known volume.
- Water Displacement Method: Used for irregular shaped samples.
- Nuclear Density Gauge: A non-destructive method that uses radioactive sources to measure density and moisture content directly in the field.
Significance of Density:
- Earthworks Control: Density tests, especially dry density and moisture content, are critical for quality control during compaction of fills, embankments, and subgrades. The achieved dry density is compared to the maximum dry density from laboratory compaction tests (e.g., as a percentage of MDD).
- Foundation Design: The density of the soil influences its strength, stiffness, and settlement characteristics, which are vital for foundation design.
- Volume Calculations: Unit weight is directly used to calculate the weight of soil in excavations or fills.
- Relative Density: For granular soils, relative density is a key indicator of the soils packing state and its susceptibility to liquefaction or settlement.
In summary, BS 1377 provides the standardized procedures for measuring various forms of soil density, which are essential parameters for classifying soils, designing civil engineering structures, and ensuring the quality of earthworks.
Exceptional Quality for Accurate Testing
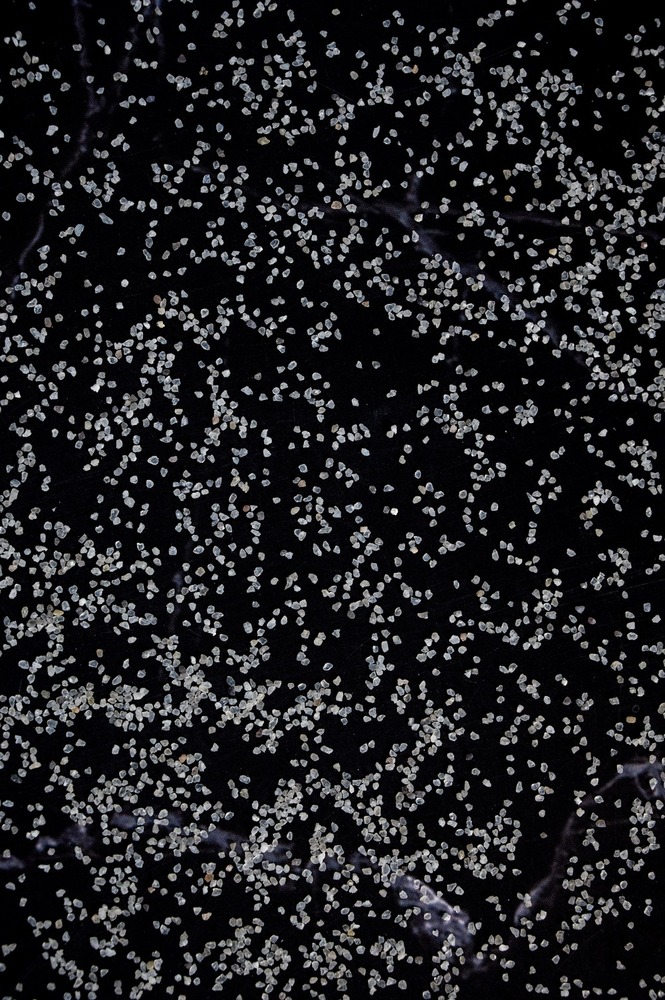
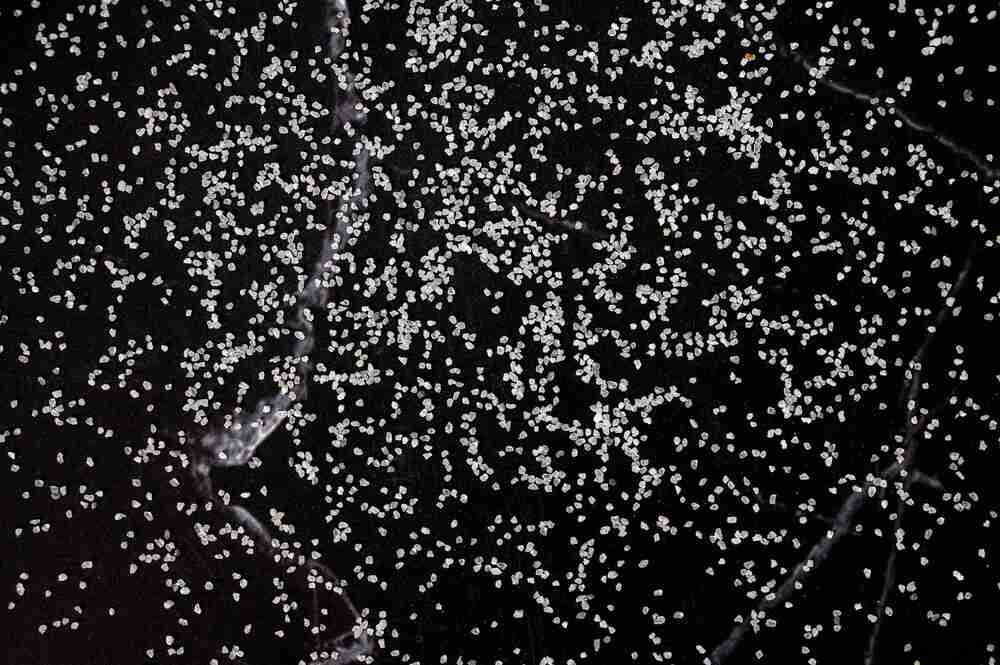
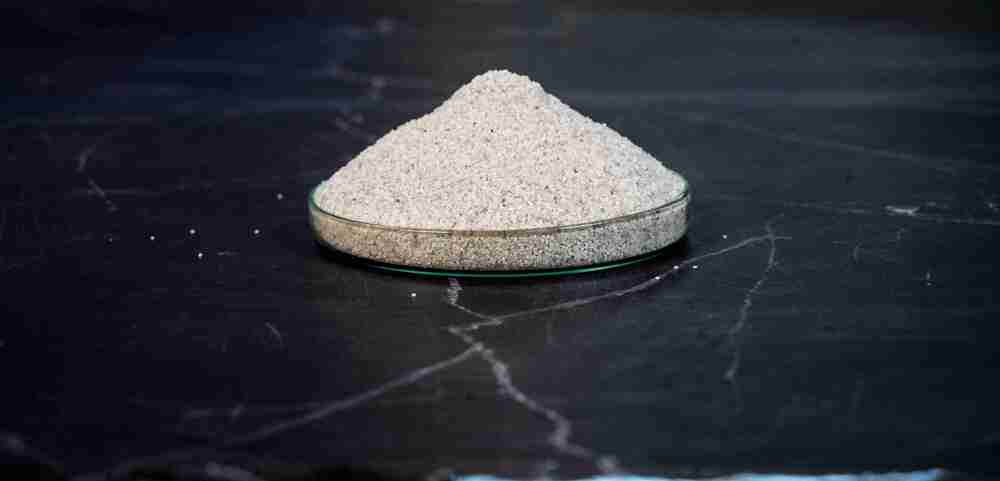
Manufactured with premium quartzite, this density sand ensures consistent particle fineness and reliable results in soil density evaluation. Complying with BS EN 1377-9 standards, it stands out for its acid-proof and corrosion-resistant qualities, making it a preferred choice in both laboratory and field environments. Its refractory attributes add to its suitability for intense testing scenarios.
Reliable Performance in Harsh Conditions
The sands chemical stability and resistance to corrosion allow it to maintain accuracy and durability when exposed to acids or other reactive substances. Its fine grain and whitish grey appearance further enhance the reproducibility of test results, making it indispensable for geotechnical engineers and researchers across India.
FAQs of BS EN 1377-9 DENSITY SAND:
Q: How is BS EN 1377-9 Density Sand used in soil testing procedures?
A: BS EN 1377-9 Density Sand is primarily utilized in laboratory soil density tests, such as the sand replacement method, to accurately determine the density or compaction of soil. Its fine particle size allows for more accurate filling of voids during testing.Q: What benefits does quartzite sand offer compared to other sand types?
A: Quartzite sand is highly valued for its acid-proof and corrosion-resistant properties, ensuring stability and minimal interference in testing environments. Its refractory characteristic also means it can withstand high temperatures without degrading.Q: When should fine, acid-proof sand be chosen for geotechnical investigations?
A: Fine, acid-proof sand should be selected when precise density measurements are necessary, particularly in environments that may expose materials to acids or corrosive substances. It is also preferred when durability under varying temperature conditions is required.Q: Where can BS EN 1377-9 Density Sand be acquired in India?
A: This specialized sand is available through authorized manufacturers and suppliers across India who adhere to international quality standards and provide certified products suitable for laboratory use.Q: What is the process for using BS EN 1377-9 Density Sand in laboratory tests?
A: The typical process involves carefully placing the fine sand into a test pit, measuring the mass of sand required to fill the void, and then using this data to calculate the soils dry density. Precision handling ensures reliable results.Q: What are the main features that distinguish this sand for industrial and laboratory applications?
A: Its acid-proof, corrosion resistance, and refractory features set it apart for use in rigorous laboratory and industrial settings. The fine grain ensures consistent measurement performance, and the whitish grey color allows easy visual inspection during testing.
Price: Â
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+












 जांच भेजें
जांच भेजें एसएमएस भेजें
एसएमएस भेजें
